EM Mudballs helped purify Amur Bay in Russia, where the sea water was polluted by the waste water from industrial area of Vladivostok.

Amur Bay in the Far-Easten seas is located near Vladivostok, and is known for its industrial area. The size of the bay is 35,000km2, 3m deep.
One of the pressing problems of the bay, especially in its northeastern part, is the inflow of pollutants in domestic wastewater from Vladivostok’s coastal enterprises.
In 2013, the volume of wastewater entering the Amur Bay amounted to about 46million m3 per year (61% the wastewater was untreated or insufficiently treated).
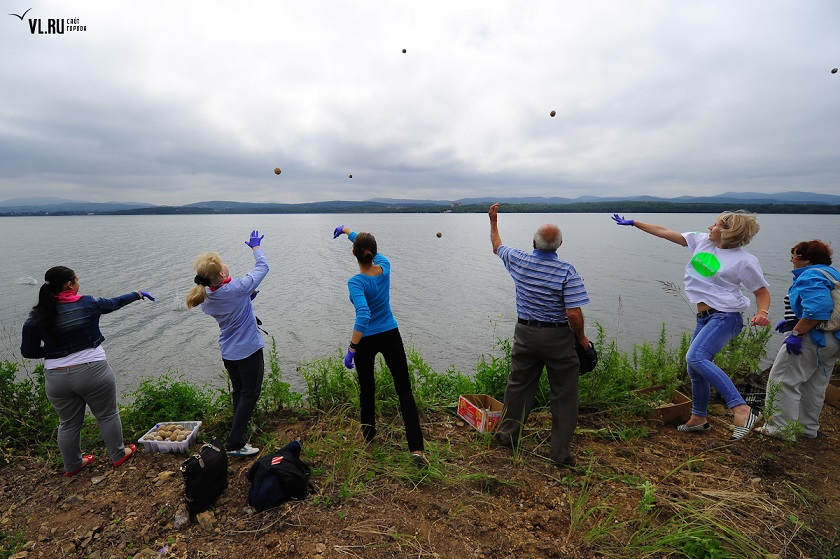
EMRO’s partner in Russia, Primorskiy EM-Center, together with the Rostok public organization and the volunteers from the Department of Ecology, the Far Eastern Federal University, prepared more than 30,000 EM Mudballs on July 11, 2016. Then, the mudballs were thrown into the bay on July 18.
The Bay was monitored for 3 months (July-September 2016):
1. Somov Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology in Vladivostok carried out the sanitary and microbiological control of the sea water quality. Samples were taken from 3 points of the bay, once in every 10 days.
2. Sanitary-chemical analysis was carried out by the sanitary-epidemiological station of Vladivostok. The water and bottom sediment samples were taken monthly from 2 points.
3. Gas-geochemical studies of sea water and bottom sediments were carried out by the Pacific Oceanological Institute. Bottom sediment samples were taken monthly from 2 sites.
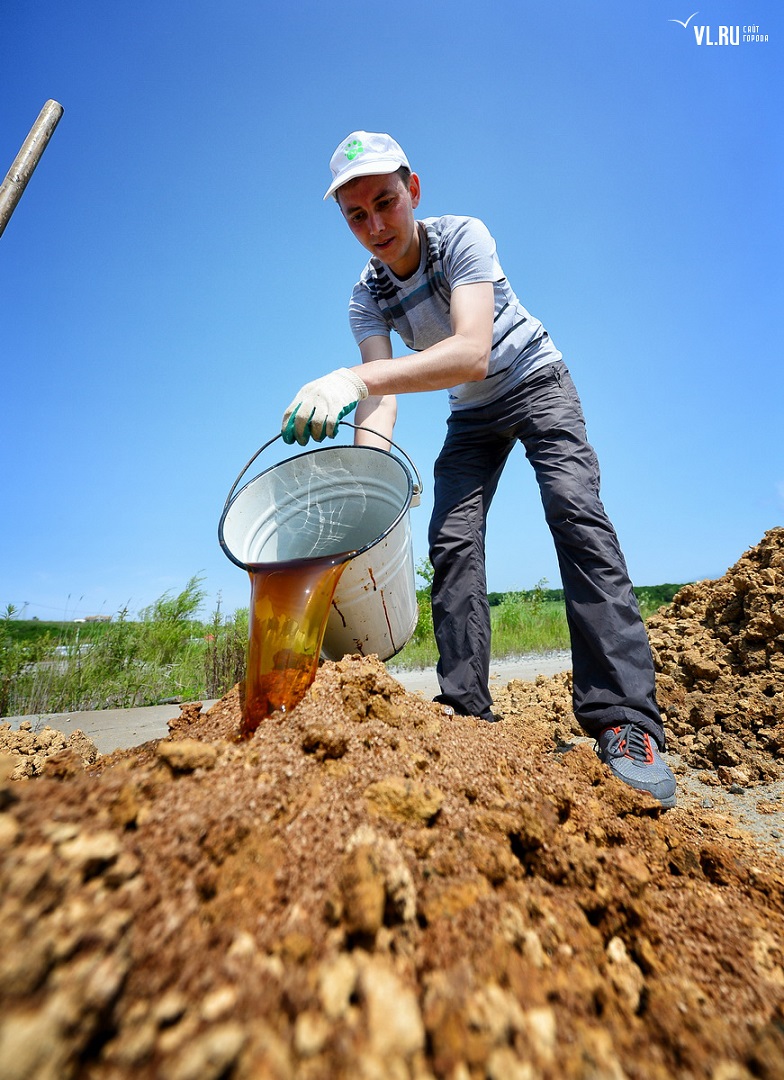

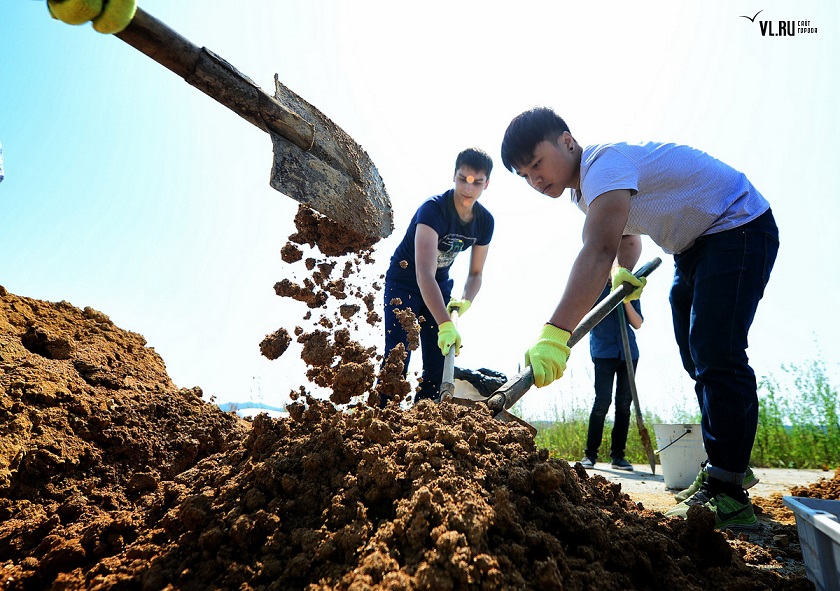
Mixing Activated EM・1 to soil
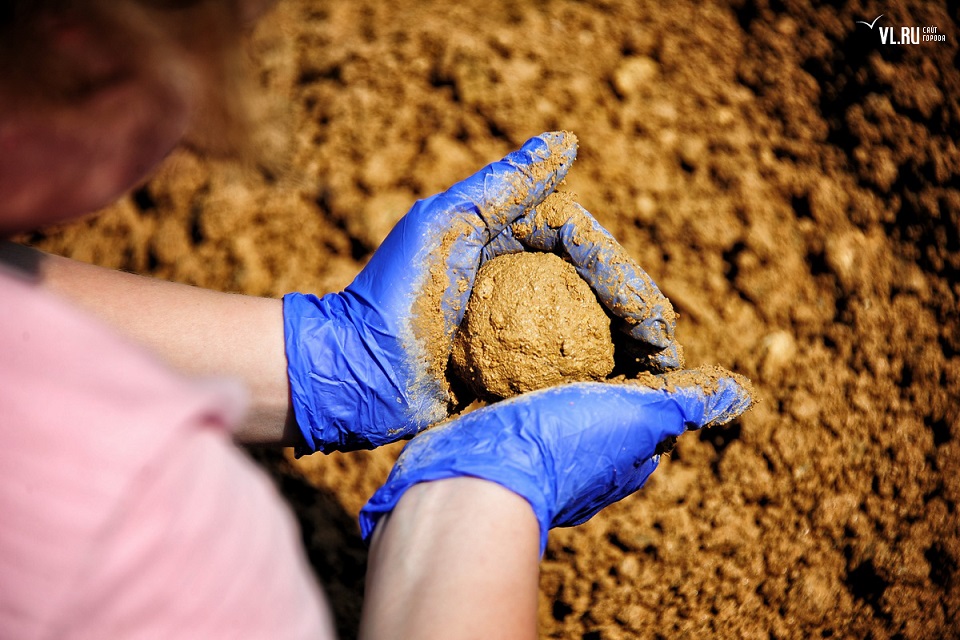

Making EM Mudballs
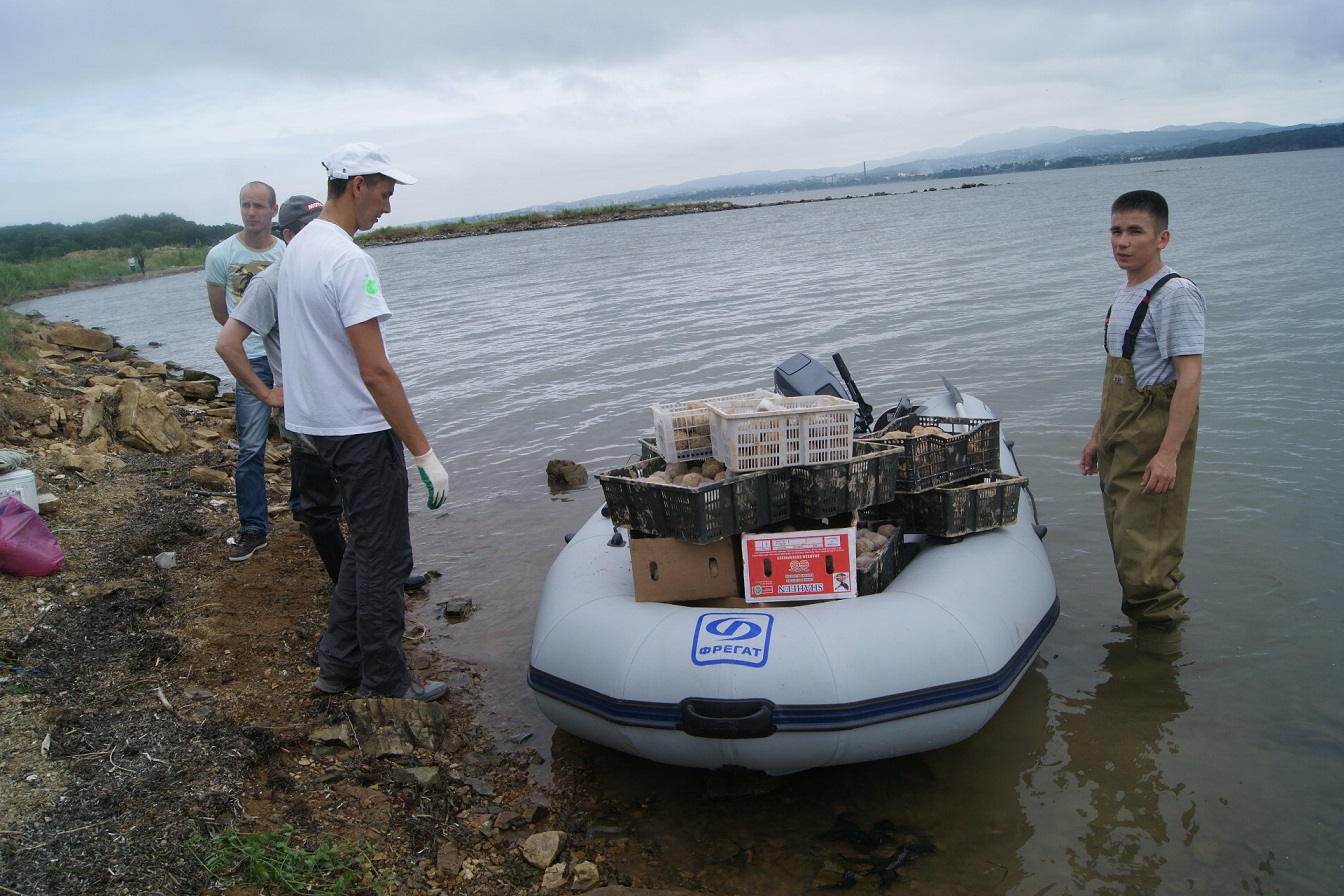

Transferring EM Mudballs by ship
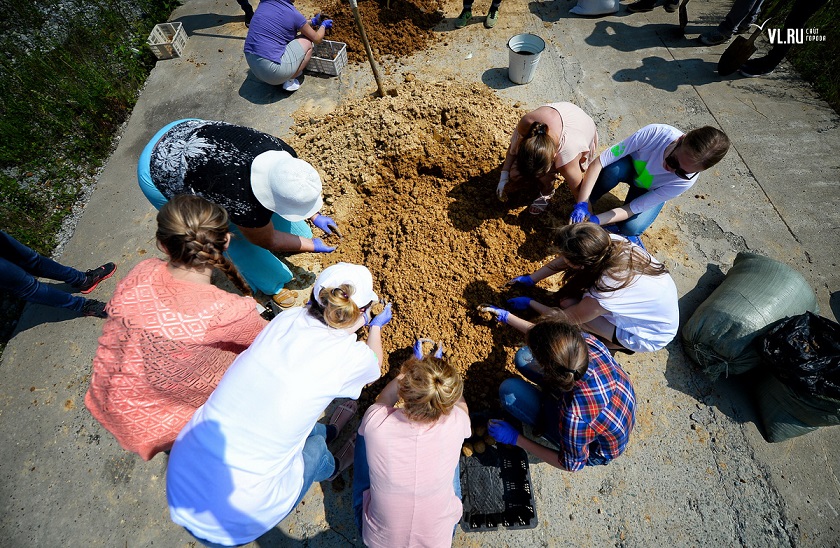

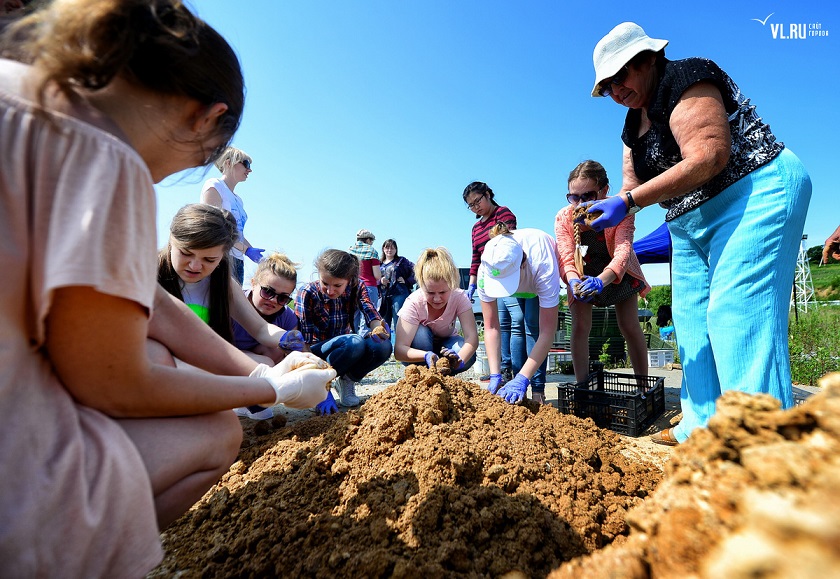
Producing EM Bokashi with Rostok public organization and volunteers from Eastern Federal University


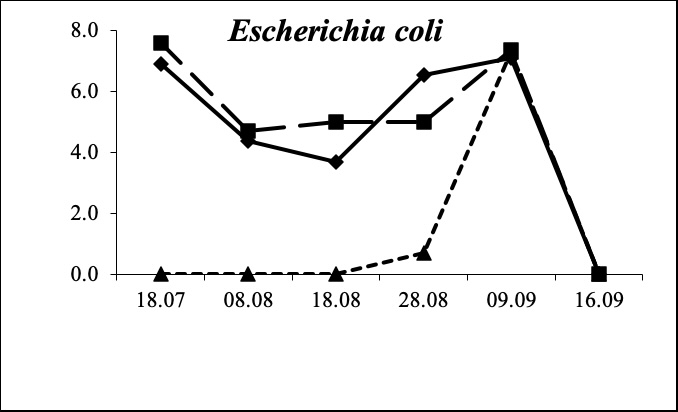
The results of microbiological studies of sea water after using EM Mudballs showed a significant decrease in concentration of enterobacteria, especially common coliform bacteria and coliphages.
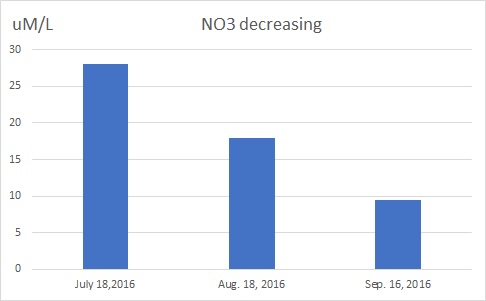
Based on the dynamics of changes in nitrate and ammonia content in bottom sediments from the points investigated in this project, compared to the points investigated in the past, it can be concluded that the process of destruction of organic matter in bottom sediments has become more active.
For further information, please contact our partner in Russia:
Mordovtseva Str, 8D, Vladivostok 690091 Russia
TEL: 8-800-333-65-95 (free call)
FAX: +7-4232-205-864
E-mail: info@em-russia.ru
Web: http://em-russia.ru/
2020.10.8 Updated